Bioenergy Conference 2023
Market Analysis
MARKET ANALYSIS
Increased Investment in Renewable Energy Drives the Market
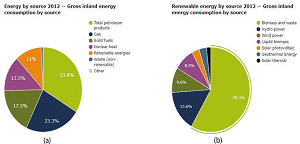
As environmental regulations are tightened around the world, the power generation industry is choosing cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy resources. Major economies around the world are focusing on developing renewable energy capacities to reduce their reliance on traditional power generation, which requires fossil fuels. Records of investment in renewable energies show that global reliance on coal and other fossil fuels is declining due to increased investment in these types of energy, such as solar, wind and geothermal. This energy is an important source of renewable energy, accounting for about 50% of the world's total renewable energy consumption, and can solve many global challenges, including environmental issues associated with the limited availability of fossil fuels. It is the only renewable energy available in all three energy sectors: electricity, heat and transportation. Therefore, most countries are investing in these energy sources, which, in turn, fuels global market demand. The global bioenergy market reached a volume of 133.58 GW in 2021. Looking forward, the publisher expects the market to reach a volume of 212.10 GW by 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.01% during 2021-2027. Keeping in mind the uncertainties of COVID-19, we are continuously tracking and evaluating the direct as well as the indirect influence of the pandemic on different end use industries. These insights are included in the report as a major market contributor. Bioenergy is a form of renewable energy that is generated from organic matter, such as biomass, biogas, and biofuel. It is widely used to produce heat, fuel for transportation, electricity, and for heating and cooking applications. It is usually obtained from natural processes and sources, such as wind and sunlight. Bioenergy is eco-friendly as it is produced from feedstock, including solid waste, agricultural waste, and liquid biofuels.
As compared to conventional energy sources, biofuels offer better energy reliability, reduced landfills, improved biodegradability, minimized carbon footprint and enhanced air quality. It can also be replenished over relatively shorter durations, thereby reducing the energy bills and reliance on fossil fuels. The rising prevalence of global warming due to growing industrial activities across the globe is creating a positive outlook for the market. Consumers are focusing on sustainable development by using bio-based fuels for power generation and biomass for developing low cost and energy effect construction materials. In line with this, the increasing environmental consciousness among the masses regarding the adverse effects of pollution and greenhouse gas (GHG) emission is also favoring the market growth. Moreover, various technological advancements, such as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with connected devices for optimizing energy usage, balancing electricity supply and predicting the performance of biomass conversion, are providing an impetus to the market growth.
Additionally, the increasing product demand to reduce air pollution and emission of GHG due to the rising instances of respiratory diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis, asthma and lung cancer, is augmenting the market growth. Other factors, including the increasing demand for biomass-based electricity generation and the implementation of various government initiatives to promote the adoption of renewable energy sources, are anticipated to drive the market further toward growth.
Growth in Transportation Sector Drives the Market
Biofuels are primarily used in place of petroleum-based fuels in transit and are considered as an important part of a strategy to improve fuel safety, mitigate climate change and support infrastructure development. Both traditional and advanced biofuels need to increase their contributions during the forecast period to meet emission targets set by various governments to delay climate change and improve energy supply safety. Aviation, on the other hand, is the second largest energy consumer in the transportation industry. The biggest hurdle in aviation is the need for high-purity, chemically stable fuels. However, some European companies will start producing kerosene from Jatropha and soon supply it to some major airlines. In addition, test flights between airlines and the US military have shown that subsequent blends of petroleum-based kerosene and bio jet fuel can be used effectively and safely. While some of the other areas where liquid biofuels can be used are rail transport. The feasibility of these fuels in this area remains unseen in the coming years. In rail transport, most rail businesses come from diesel towing, and biodiesel has the potential to be a viable alternative fuel for running trains. Hydrothermal Upgrading (HTU) Diesel & Biomass to Liquid (8t) used in other power generation systems such as biogas, bio-methane, bioethanol and biomass.
Key Insights & Findings from the Report:
- According to our primary respondents’ research, the Bioenergy market is predicted to grow at a CAGR of roughly 7.3% during the forecast period.
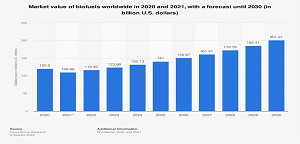
- The Bioenergy market was estimated to be worth roughly USD 103.5 Billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 157.9 Billion by 2028; based on primary research.
- On the basis of region, Asia Pacific is projected to dominate the worldwide Bioenergy market.
Benefits of Purchasing Bioenergy Market Reports:
- Customer Satisfaction: Our team of experts assists you with all your research needs and optimizes your reports.
- Analyst Support: Before or after purchasing the report, ask a professional analyst to address your questions.
- Assured Quality: Focuses on accuracy and quality of reports.
- Incomparable Skills: Analysts provide in-depth insights into reports.
Segmentation of the Global Bioenergy Market:
- Product Type
- Feedstock
- Application
- Region
COVID-19 Impact Analysis:
The COVID-19 outbreak has affected various industries worldwide. Governments across the world implemented strict lockdown measures and social distancing norms in order to restrict the swift spread of the pandemic. Manufacturing facilities around the world were shut down during the initial stages of the pandemic. Moreover, the economic crisis after the pandemic might lead to a significant delay in the commercial roll-out of the electronics industry. Small and medium-scale companies are the backbone of technology providers and are witnessing a steep drop in revenue since the emergence of the pandemic in 2020. Hence, market players faced numerous challenges as disruptions in the supply chain were observed. However, things will improve in the second half of 2022 as more supplies will come online.
The impact of COVID-19 on the market demand is considered while estimating the current and forecast market size and growth trends of the market for all the regions and countries based on the following data points:
- Impact Assessment of COVID-19 Pandemic
- Quarterly Market Revenue Forecast by Asia Pacific 2020 & 2021
- Key Strategies Undertaken by Companies to Tackle COVID-19
- Long Term Dynamics
- Short Term Dynamics
The Report on Bioenergy Market Highlights:
- Assessment of the market
- Premium Insights
- Competitive Landscape
- COVID Impact Analysis
- Historic Data, Estimates and Forecast
- Company Profiles
- Global and Regional Dynamics
Regional Analysis:
Europe Holds Largest Market Share. Europe accounted to have substantial growth for Bioenergy Market in 2021. Emerging countries such as India and China have introduced strict regulations to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. This is an important factor driving market growth. In Japan, the use of timber for energy is expanding, two-thirds of the country is covered with forests, and about 100 million m³ of timber is regenerated annually. In 2018, about 9 Mt of solid wood biomass was used for wood and energy, of which more than 75% was wood chips. China, India, Australia, South Korea and Southeast Asia are the largest consumers of this type of energy in the Asia Pacific region.
List of Prominent Players in the Bioenergy Market:
- Envi Tec Biogas AG
- Babcock & Wilcox
- Orsted A/S
- Fortum Oyj
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation
- Pacific Bioenergy Corp
- Royal Dutch Shell PLC
- BP PLC
- Enerkem
- MVV Energie AG
Major Bioenergy Associations around the Globe
- Bioenergy Association
- World Bioenergy Association
- Biofuels and Biomass Energy (bioenergy): Associations & Societies
- Bioenergy International AG
- Bioenergy Council of India
- Renewable energy Organizations and Associations
Major Bioenergy Companies around the Globe
- Bio product companies
- Biofuels Digest
- Green Plains Renewable Energy
- Fulcrum Bioenergy
- Sweetwater Energy
- Elevance Renewable Sciences
- Abengoa Bioenergy
- Renewable Energy Group
- Sapphire Energy
Target Audience:
- Bioproduct companies
- Bioenergy Associations
- Bioenergy Researchers
- Bioenergy Industry
- Bioenergy Scientists
- Nuclear energy Engineers
- Bioenergy technology Engineers
- Chemical Engineers
- Renewable energy Organizations and Associations
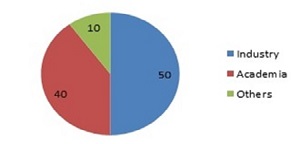
In total, percentage of attendees from various sectors as follows
Market Analysis:
The demand for renewable energy is growing enormously. From the evidence available today, we believe that biofuels could, with developments in technology and favourable policy constitute up to 30% of the world transport fuel mix by 2030. The advantages of bioenergy – whether in greenhouse gas benefits, energy security or rural development-mean that many governments are keen to foster the industry through current phases of technology development to deliver material scale and reduced costs.
Our belief is that the industry can be developed sustainably, provided appropriate feedstock’s are grown, which do not adversely compete with food, using good land management to minimize environmental impact. This will require development of appropriate sustainability standards; it will not be easy, but by engaging in the industry, responsible businesses will work out appropriate business models and want to see enforcement of standards across the industry. This paper sets out the characteristics of the global fuels market, the significance of joint industry studies with car manufacturers and the choices around land use that society must make. The approach taken by BP is then described whereby guiding principles have been defined to set the boundaries of our impact on ecosystems.
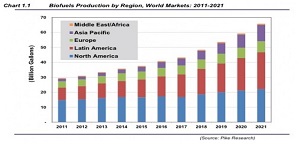
Characteristics of the biofuels market: its size and growth rate, the world is in a state of biofuels fever. In 2006 biofuel constituted 49 bnlitres, Or 3%, of the 1,600 billion litre market for gasoline and diesel fuel. By 2015 the biofuels market is likely to have tripled to 155 billion litres. In practical terms that is an increase of around 10 billion litres per year over ten years. In terms of current ethanol yields of 5,250ltrs / ha, this equates to an increase of land use for biofuels of approximately 17,000 square km per year. The bulk of the global demand for ethanol and biodiesel comes from a few major regions. The USA accounted for very nearly 50% of global ethanol consumption in 2006, with Brazil taking 36% of global volumes.
The EU accounted for 75% of global biodiesel consumption in 2006. The reason why we believe the feverish rate of growth is likely to materialize is because, with no carbon beneficial substitutes available in the near term, biofuels are being promoted by governments. Clear examples of this are the trends of regulations in the EU, and the intentions announced in the US. BP is already a major player in the global biofuels market. In 2006 BP blended 3,016 million litres of ethanol into gasoline – a 25% increase on the previous year. Thus BP is already well exposed to the biofuels fever – and the theme of this paper is to suggest how the industry can tap the heat of the fever in a positive sense.